How Helminth Parasites Induce Chronic Gut Issues and Diarrhea
Oct 17, 2023
Introduction
The human gut is a dynamic ecosystem teeming with microorganisms, some of which can cause significant gastrointestinal distress.
Among these, helminth parasites, or worm-like parasites, have attracted considerable scientific attention due to their capacity to induce chronic gut issues and persistent diarrhea.
In this article, we will delve into the world of helminth parasites, including global prevalence estimates, to understand how specific species contribute to these unsettling digestive health concerns.
Understanding Helminth Parasites
Helminth parasites are multicellular organisms that reside in the human intestines, where they feed off nutrients and can result in a range of health issues.
Scientific research and epidemiological data have identified specific species known for their potential to induce chronic gut problems.
Let's focus on a couple of well-known helminth parasites, with reference to global prevalence statistics:
-
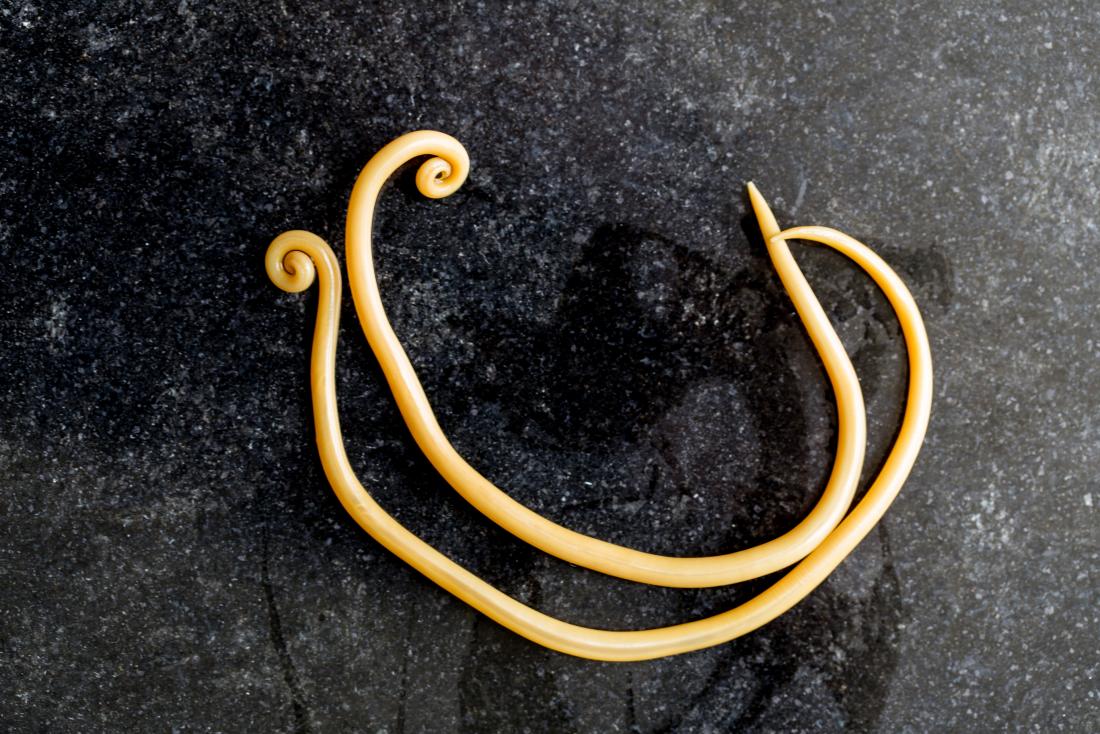
Ascaris lumbricoides: The Giant Roundworm
Ascaris lumbricoides, responsible for ascariasis, is among the most prevalent intestinal parasites globally.
According to this paper, it is estimated that over 1.2 billion people are infected with Ascaris lumbricoides worldwide.
This and several other scientific studies have highlighted the ability of this parasite to cause gastrointestinal distress.
In cases of heavy infestation, these giant roundworms can obstruct the intestines, leading to chronic abdominal pain, cramps, and diarrhea.

-
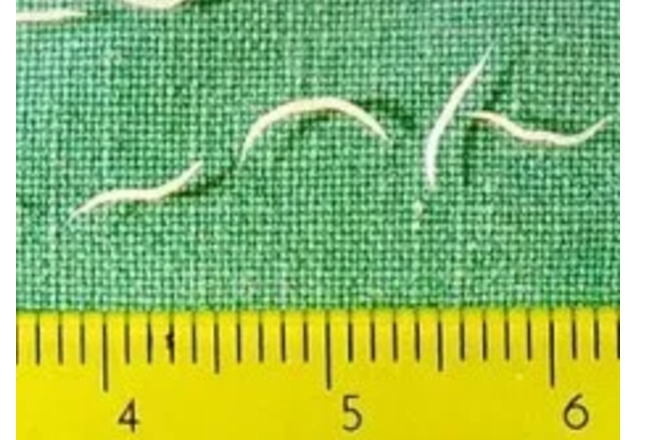
Trichuris trichiura: The Whipworm
Trichuris trichiura, or the whipworm, is another well-documented helminth species associated with gastrointestinal issues.
According to the WHO, it is estimated that nearly 600 million people worldwide are infected with Trichuris trichiura.
Research has shown that whipworms attach themselves to the large intestine's wall, causing inflammation and damage.
This can result in chronic diarrhea, often accompanied by mucus and blood, as well as abdominal discomfort.
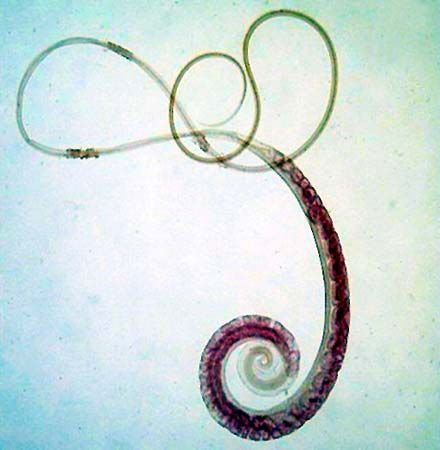
3. Strongyloides stercoralis: The Threadworm
Strongyloides is a genus of parasitic nematode worms that can infect humans.
This parasitic infection, known as strongyloidiasis, is particularly intriguing due to its unique life cycle and its connection to gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea.
Mechanisms of Helminth-Induced Gut Issues
With reference to scientific literature and global prevalence statistics, let's explore the mechanisms through which specific helminth parasites like Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, and Strongyloides stercoralis can lead to chronic gut problems and diarrhea:
Structural Damage: Ascaris lumbricoides can cause physical obstructions in the intestines, leading to chronic abdominal pain, cramps, and diarrhea.
Inflammation and Tissue Damage: Research has shown that Trichuris trichiura's attachment to the large intestine's wall leads to inflammation and damage, resulting in chronic diarrhea, often accompanied by mucus and blood.
Nutrient Competition: Helminth parasites can compete with the host for nutrients, potentially causing malnutrition, weight loss, and chronic fatigue, as outlined in various studies.
Altered Gut Microbiota: The presence of helminths can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota, leading to imbalances and gastrointestinal issues.
Release of Toxins: Helminths may release toxins during their life cycle, which can damage the intestinal lining and contribute to diarrhea and other digestive problems.
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of helminth infections typically involves analyzing stool samples or conducting blood tests to identify the specific parasite, as recommended by the WHO.
However, these detection methods are often inadequate and can result in many infections being missed. For this reason, it can be a good idea to take preventative action to ensure that you do not become susceptible to infection.
While treatment involves anti-helminthic medications, as per WHO guidelines, many medications have limitations to their efficacy and natural cleansing alternatives can prove more effective.
Prevention
Preventing helminth infections includes practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with contaminated soil, and consuming properly cooked food, as suggested by public health initiatives and research in the field.
However, aside from these basic lifestyle foundations, it's a good idea to engage in yearly cleansing to stave off any potential presences before they may become an issue.
...
If you need help understanding how you might benefit from cleansing, check out our quiz.






